Two revolutionary trends have taken center stage in healthcare’s digital transformation journey: the migration of healthcare services to the cloud and the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
These shifts are not just technological upgrades; they represent a fundamental change in how healthcare is delivered, promising to make it more accessible, efficient, and personalized than ever before.
The Cloud: A New Home for Healthcare
The migration of healthcare services to the cloud responds to the increasing demand for more scalable, flexible, and secure data management solutions. Cloud computing offers several advantages over traditional on-premises IT infrastructures, including cost-effectiveness, enhanced collaboration, and improved data security. By leveraging the cloud, healthcare providers can store vast amounts of medical data—ranging from patient records to complex imaging files—securely and access them from anywhere, at any time. This accessibility is crucial for timely decision-making and providing continuous patient care, even in remote or underserved areas.
Additionally, the cloud enables healthcare organizations to deploy and scale up their services quickly, adapting to changing demands without the need for significant upfront investments in IT infrastructure. This flexibility is vital in a field where the rapid deployment of new services or expansion to meet emergency needs can save lives.
AI: The Engine of Innovation in Healthcare
AI technologies, living in the cloud, are transforming healthcare from within. These intelligent systems analyze vast datasets to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend treatments, making healthcare more proactive and personalized. AI applications in healthcare range from diagnostic tools that can detect diseases with unprecedented accuracy to chatbots that provide immediate, AI-driven consultations.
One of the most significant advantages of AI in healthcare is its ability to handle the enormous amounts of data generated daily. AI algorithms can sift through this data, identifying trends and insights that would be impossible for humans to discern, leading to earlier diagnoses and more effective treatments. Furthermore, AI can automate routine tasks, from patient scheduling to the analysis of diagnostic images, freeing healthcare professionals to focus on more complex and compassionate patient care.
The Synergy of Cloud Computing and AI in Healthcare
The true potential of AI in healthcare is unlocked when it operates within the cloud. This synergy allows for the seamless integration of AI tools across different healthcare services, making it easier to deploy, update, and scale these solutions as needed. The cloud not only provides the computational power necessary for running complex AI algorithms but also ensures that these tools are always available and up to date, thanks to its centralized nature.
Cloud-based AI applications can also facilitate real-time data sharing between healthcare providers, enabling a more collaborative approach to patient care. For instance, AI-driven insights derived from patient data can be shared across a network of providers, ensuring that treatment decisions are informed by the most comprehensive and current information available.
Unlocking the Potential of Data with AI
Achieving the full benefits of AI in healthcare hinges on the maturity of data derived from an integrated analytics system. A comprehensive strategy focusing on data unification, collaboration, and governance is essential. Such an approach offers providers a valuable opportunity to assist in unlocking the potential of data through AI, facilitating the transformation of data into insights and insights into actionable strategies. This progression is key to driving innovation and growth within the healthcare sector.
A Unified Vision for Healthcare in the Cloud
The migration of healthcare to the cloud, supplemented with AI, represents a pivotal moment in the sector’s evolution. This transition promises to make healthcare more accessible, efficient, and personalized, ultimately leading to better patient and clinician outcomes. However, realizing this potential will require careful navigation of the technical, regulatory, and ethical challenges that accompany these technological advancements. As healthcare continues its journey to the cloud, the focus must remain on leveraging these technologies to enhance, rather than replace, the human touch that lies at the heart of patient care.
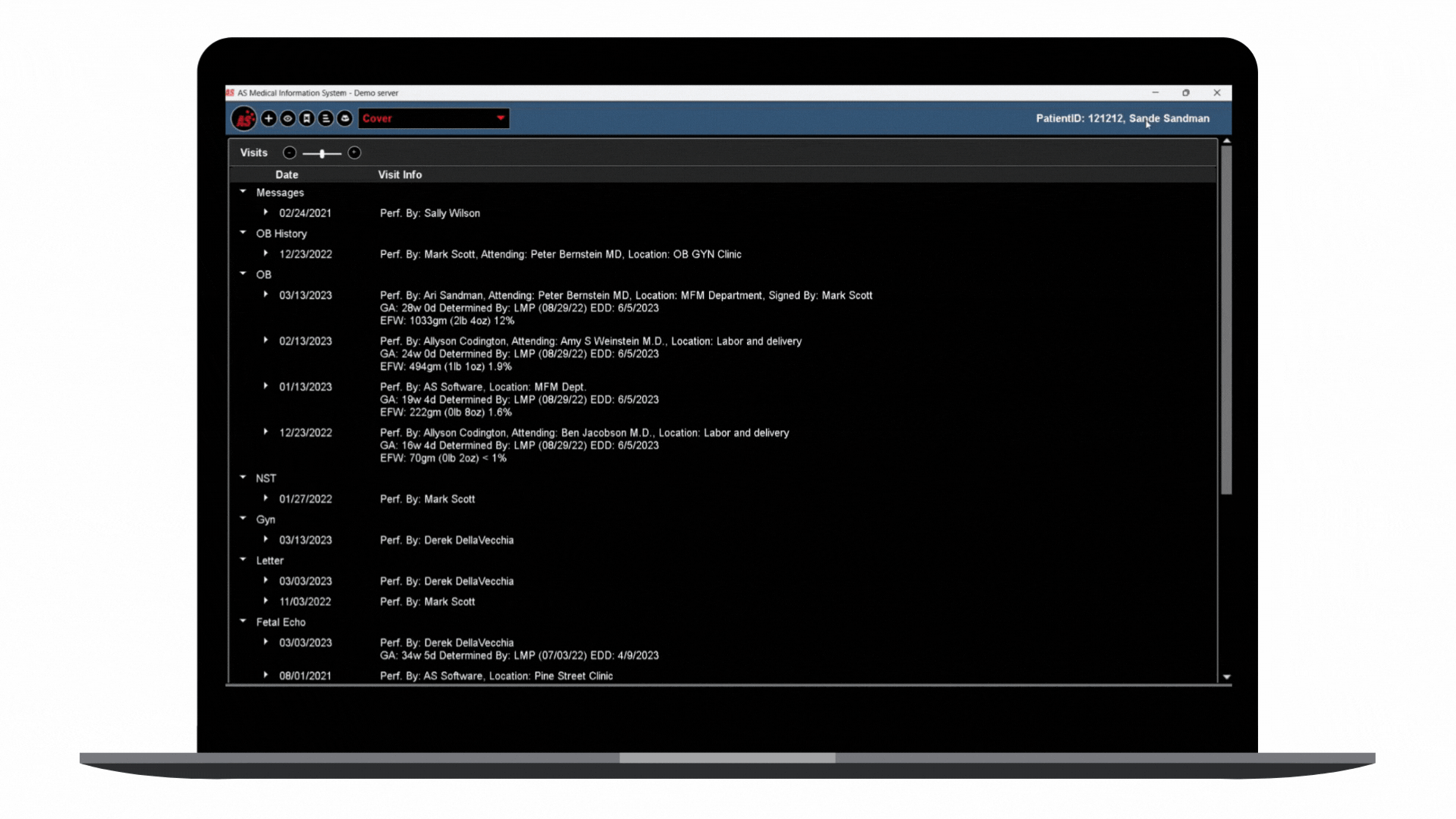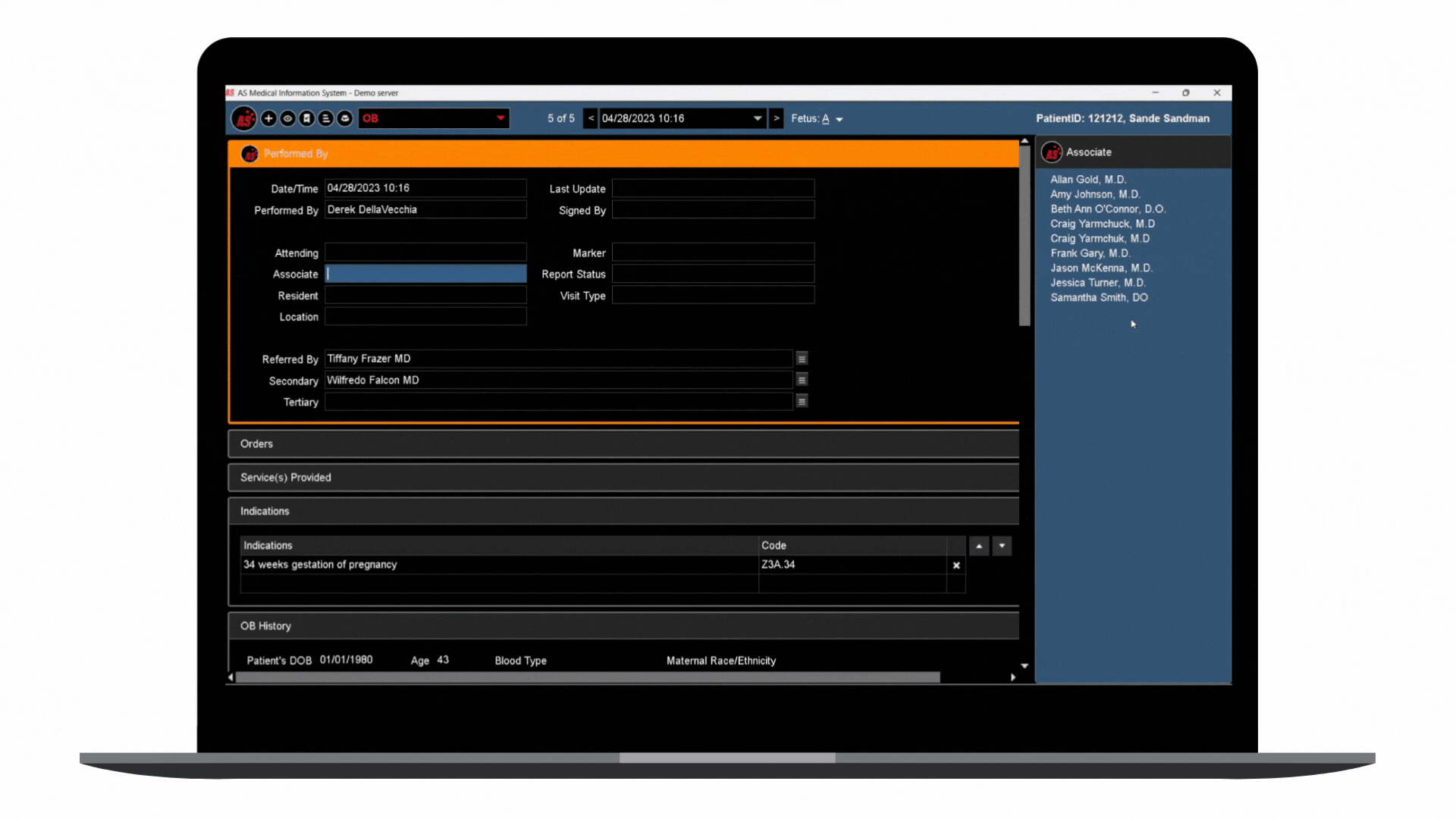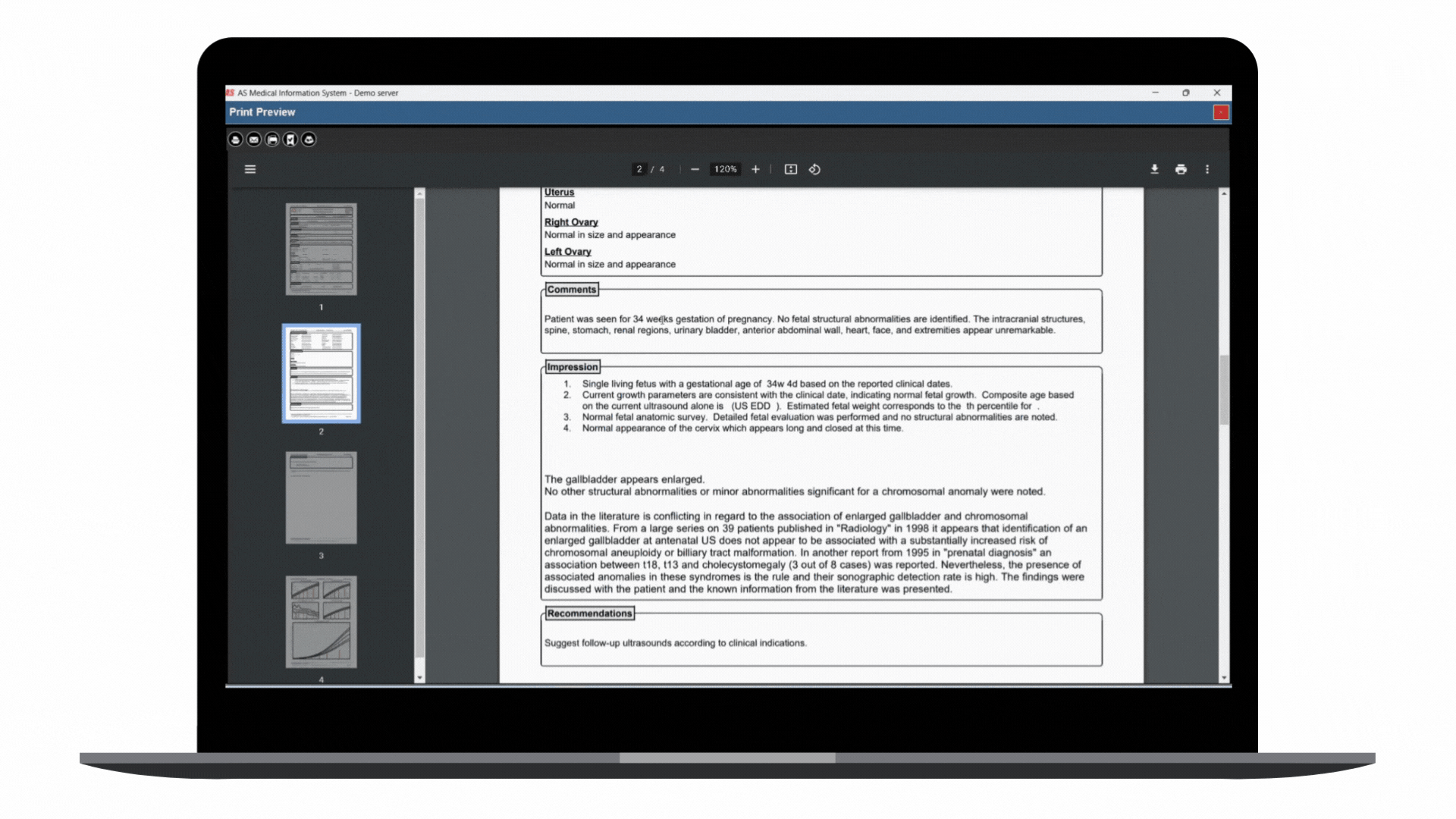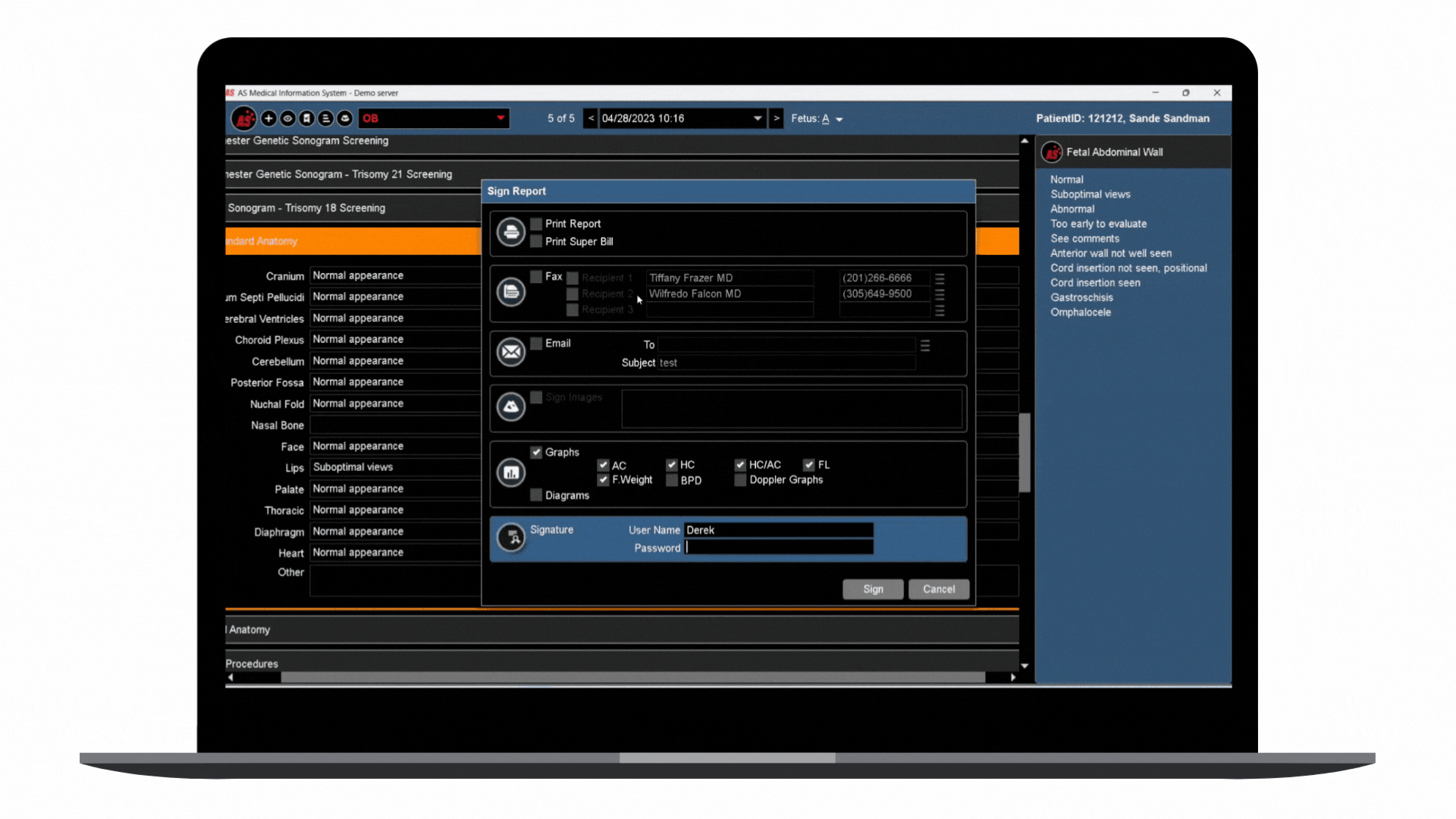
In step with this digital transformation, embracing a modern, cloud-first strategy for automating enterprise ultrasound systems with integrated AI represents a future forward. It supplements the approach to the healthcare cloud. It pushes the limits of diagnostic proficiency and improves overall enterprise reporting and the management of extensive datasets prevalent in ultrasound specialties. This shift to a more sophisticated platform unites with the broader transition of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to the cloud, optimizing clinical workflows and solidifying the ease of data retrieval and utilization.
This ultrasound management and operations modernization creates a unified ecosystem that provides substantial advantages for healthcare professionals and, most importantly, for the patients they serve.